A joint paper, coordinated by Anastasiia Volovikova from KIT, has been accepted for publication in the Research and Review Journal of Nondestructive Testing (ReJNDT). The authors work together in the DFG network “Towards a holistic quality assessment for guided wave-based SHM”.
Abstract:
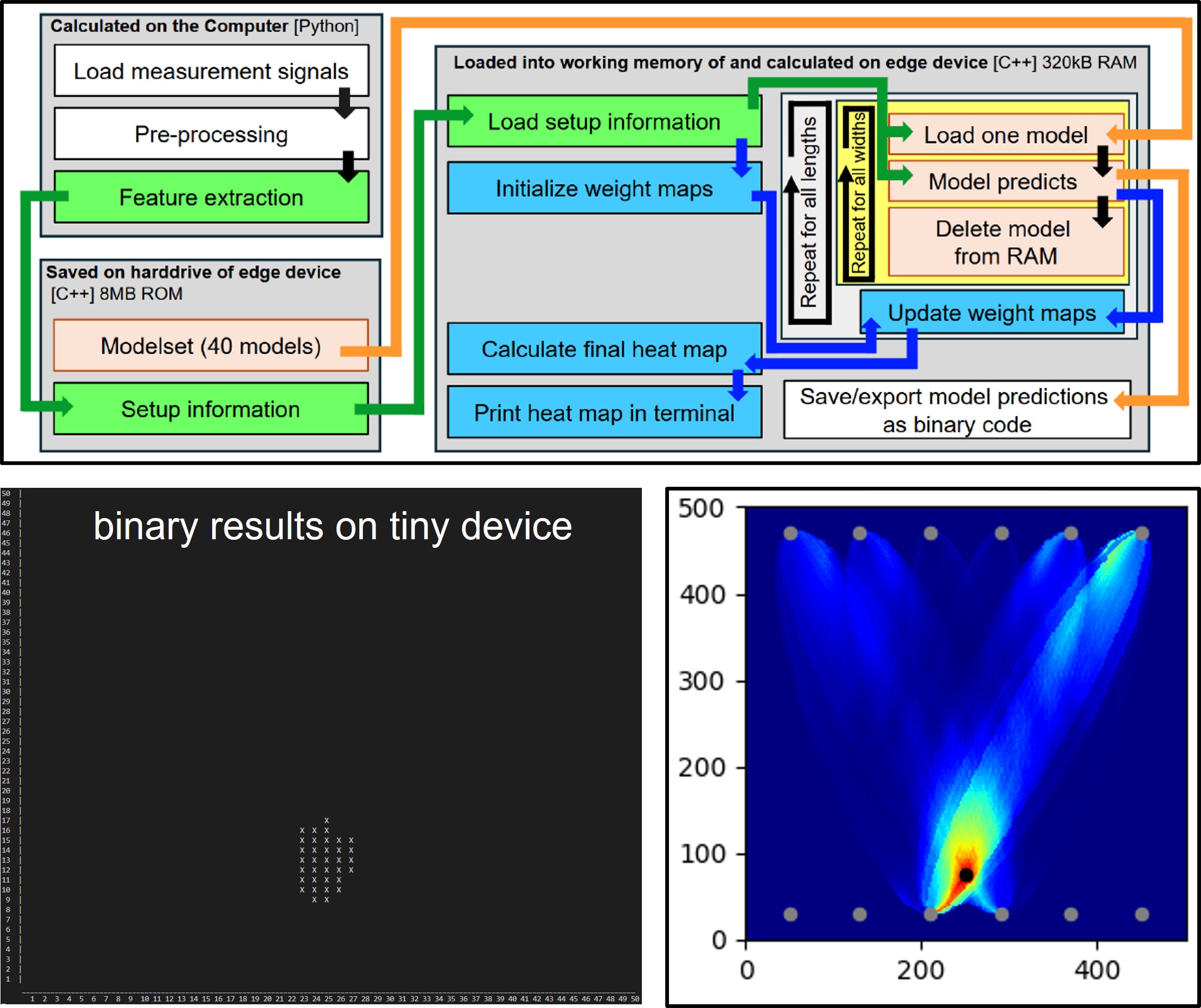
The continuous monitoring of structural integrity is crucial, as imperceptible damage may appear at any point throughout a structure’s lifespan. Several Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) technologies have been developed so far to detect and assess defects in structures. Deep Learning is a common tool for processing data obtained with SHM systems. Although many artificial intelligence-based SHM technologies exist already for damage detection, only a few are focused on damage localization. Existing localization approaches are limited through them being applied on defined simple structures and requiring a large amount of data, which is usually unavailable in practical applications. In this work, measured data from guided ultrasonic wave propagation is used to determine the location of damage in a composite stiffened structure representative of fuselage segments. A novel artificial intelligencebased approach for damage localization is presented and tested with a feed-forward as well as a convolutional neural network. Both architectures show that localization is possible. The accuracy is then analyzed with the probability of localization method and compared to existing non-artificial intelligence-based approaches. These results make it possible to define the minimum damage that can be correctly localized.
More information:
Volovikova, A.; Freitag, S.; Schackmann, O.; Memmolo, V.; Bayoumi, A.; Mueller, I. & Moll, J., Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach for Damage Localization in Ultrasonic Guided Wave-Based Structural Health Monitoring, Research and Review Journal of Nondestructive Testing, 2024 (accepted in November 2024)